Local Food System Development in Mississippi: How Local Governments Can Support Farmers Markets
Creating a vibrant, local food system in Mississippi is an important economic development strategy. A significant part of that is recognizing the growing demand for fresh, local foods and then working to support the development of markets to bring local food producers together with consumers. Recently, increased demand for fresh, local food has boosted the efforts of businesses and communities to coordinate easier access to local food markets. One of those markets in Mississippi communities is farmers markets. Between 2010 and 2017, the number of farmers markets increased from 54 to 95. A strong, continued growth in the number of farmers markets has emerged in Mississippi (see Figure 1).
The purpose of this publication is to explain the benefits associated with establishing farmers markets and describe the factors that contribute to successful farmers markets in Mississippi. The publication also discusses ways that local governments can support farmers markets. Information is also provided on an approach within the Mississippi State University Extension Service that supports local food systems using a cross-disciplinary, statewide team.
Farmers Markets Are Important to Economic Development
Economic development is a broad term related to the benefits communities gain from the recruiting and retaining businesses and industries. In this publication, economic development refers to the benefits to a community from establishing a farmers market. Farmers markets offer several benefits to communities, including the following:
- Consumers have access to local food products that they might not otherwise have.
- Food products are often high-quality in terms of freshness.
- Consumers like having access to and interaction with local producers, which facilitates discussion about pesticides, herbicides, and other production topics.
- Consumers enjoy knowing they are purchasing locally, which benefits local food-based producers.
- Small farms that supply farmers markets can attract affluent immigrants to the local area.
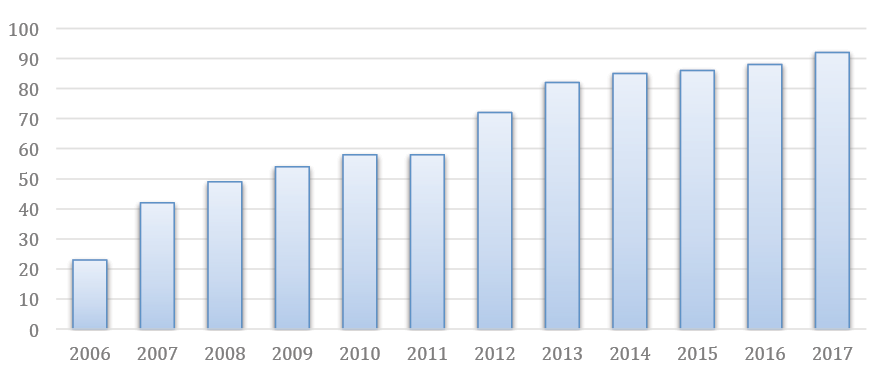
Figure 1. Farmers markets in Mississippi.
Capturing these benefits requires significant planning and consistent management of the farmers market. Market managers in Mississippi often share best practices and learn from one another. Local governments also play a key role. Collaboration among local governments and farmers market managers is key to market development.
The Mississippi Department of Agriculture and Commerce (MDAC) hosts the Mississippi Farmers Market Managers Annual Conference. At the April 2017 conference, improving farmers markets was a key topic. MSU Extension Service facilitated a group discussion among market managers to identify continued challenges and ways to overcome them.
Improving Farmers Markets Is a Process
The market-improvement model can be advantageous to improving farmers markets. The model includes collaboration, organization, communication, and building relationships, which result in successful markets (see Figure 2).
Improvement begins with collaboration. Sharing best practices for farmers markets is a necessary part of bettering all markets. Market managers can implement ideas that work and make adjustments to those that do not. This combination of collaboration, organization, and communication is vital toward improvement.
Market managers can adopt new best practices and implement them with the support of their advisory councils or others who govern the work of local farmers markets. This process builds partnerships among institutions, consumers, and producers. Implementing new ideas across the local food-supply chain can create innovative approaches to improving farmers markets.
Successful farmers markets tend to move quickly on new ideas and learn how consumers respond. This process can be repeated each time market managers collaborate to examine strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats they have observed while working to develop their markets. Online tools (e.g., email or social media) also can increase collaboration and enhance communication in terms of frequency of interactions and the quality of those interactions.
Farmers Market Success: 9 Factors
Within the farmers market-improvement process, several success factors have emerged. Each factor relates to one of the market-improvement process steps listed in Figure 2. For farmers markets to be successful, they could consider the following:
- Dedicated hospitality toward all shoppers, maintaining a safe and clean environment at all times.
- A convenient location and easy access for consumers, including ample parking.
- A wide variety of products such as baked goods, produce, and crafts to attract a larger pool of consumers.
- Participation of young people in events held at farmers markets to increase engagement. This has been proven effective especially when combined with educational or entertainment events. In some cases, young people volunteered to assist consumers with their purchases.
- Quality customer service at the market. It is also recommended that vendors understand how to effectively manage customer relations to build connections with their buyers.
- Market managers remaining on-site during the market to welcome newcomers and create activities for attendees.
- Establish a focused theme by highlighting a particular commodity. Children’s activities and other entertainment options can be built from the chosen theme. Dairy Day is an example of a themed event.
- A unique mascot or character to use in farmers markets advertisements on websites and social media.
- Informational material such as nutrition education, healthy recipes, and cooking ideas at markets can be beneficial to consumers.

Figure 2. The market-improvement process model.
Farmers Markets Assistance: 9 Needs
MSU Extension also facilitated a discussion of existing issues and needs and how progress can be made toward improving farmers markets. Some of the unmet needs that were discovered include the following:
- Training for social media management, signage, business card design, and visual merchandising were among the most needed educational programs.
- Attracting a diverse set of vendors to increase the appeal to more consumers.
- Additional training on using websites, blogs, and other online marketing tools.
- More information to help young people understand local food production.
- Further training on nutrition and healthy eating habits.
- More information on federal nutrition programs, including the Supplemental Nutrition Assistance Program (SNAP) and the Expanded Food and Nutrition Education Program (EFNEP). SNAP works with limited-resource populations to provide nutrition education, cooking demonstrations, cooking classes, school and community gardens, and assistance in making the healthy choice the easy choice through policy, system, and environmental changes. SNAP issues eletronic benefit transfer (EBT) cards, which can be used at some markets. EFNEP provides direct nutrition education to limited-resource families to help improve diet quality and physical activity.
- Increased cold storage for meat and dairy products to remedy the limitations at each market. Managers indicated grants would be a feasible vehicle to provide this type of equipment.
- Explanation of local and state regulations to vendors, especially regulations about food safety labeling and processing.
- Future work and training to focus more on learning about food hubs and understanding branding requirements and other regulations.
Local Governments Can Help
The demand for local foods is growing in Mississippi, and the number of farmers markets continues to increase. Vendors noted local foods such as muscadines, organic vegetables, eggs, fruit, butter beans, and some meats remain in high demand. Local government organizations can play a vital role in creating, growing, and sustaining farmers markets to meet Mississippi consumer demand. Local governments can take the following steps:
- Determine if a farmers market is needed in a specific local area.
- Create a plan regarding the services the city/county can provide before the market opens.
- Work with emergency managers to ensure facilities are kept safe and accessible.
- Provide legal assistance to determine any liability that needs to be addressed and provide options for liability coverage.
- Facilitate dialogue between state agencies and the local planning committee, especially when it comes to understanding regulations about food safety and processing.
- Provide a facility or space for the farmers market. The facility should be easily accessible and affordable to sustain a farmers market.
- Provide free garbage collection, parking, and police support.
- Provide access to public restrooms either directly on-site or adjacent to the market.
- Provide funding for staff members to assist the farmers market manager.
- Provide advertising by placing links to the farmers market website and social media channels on the city or county website.
- Support educational programs on preparing healthy foods, growing vegetables, or other relevant topics.
Taking the Next Step
This publication provided information on some success factors, existing needs for growth, and ideas for local government support of farmers markets. Providing such information can generate increased collaboration between farmers market managers and local elected officials. This is an important aspect of market development as it can lead to sizeable benefits for consumers, local governments, and local food producers. To further economically develop farmers markets and local food systems in Mississippi, MSU Extension is working to bring about new programs and efforts.
The first step is to find new ways to support the collaboration between farmers markets and local governments. One of the best ways to facilitate this type of collaboration is to identify the benefits that could accrue from greater collaboration. Benefits in this instance refer to the economic impact of farmers markets. Some work has been done to measure the economic impact of farmers markets in Mississippi as a way of documenting the benefits of developing local food systems.
The economic impact of farmers markets in Mississippi was estimated by collecting sales data from 26 of the 52 farmers markets that existed in 2010. Results indicated approximately $950,000 in sales. These direct sales generated another almost $670,000 in indirect benefits. As a result, the total economic impact of these 26 farmers markets was more than $1.6 million. With only 50 percent of markets reporting in this study, $1.6 million served as a conservative estimate of the total economic impact of farmers markets in Mississippi in 2010.
Fast-forward to present day, and Mississippi has nearly 90 farmers markets. The economic impact of this number of farmers markets on the state’s economy and the management of local food systems will be examined more broadly.
To learn more about the work that is being done to support local food systems in Mississippi, visit extension.msstate.edu.
References
Hughes, D.W., C. Brown, S. Miller, and T. McConnell. 2008. Evaluating the Economic Impact of Farmers Markets Using an Opportunity Cost Framework. Journal of Agricultural and Applied Economics, 40, 1 (April 2008): 253-256.
Publication 3126 (POD-12-23)
By Rachael Carter, PhD, Extension Specialist II, Extension Center for Government and Community Development; James Barnes, PhD, Associate Extension Professor, Agricultural Economics; and Chance McDavid, Project Director, Stennis Institute of Government and Community Development.

The Mississippi State University Extension Service is working to ensure all web content is accessible to all users. If you need assistance accessing any of our content, please email the webteam or call 662-325-2262.




